Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Surfactants
Surfactants, or surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension between two substances, such as liquids and solids. They are commonly used in detergents, emulsifiers, and foaming agents. Surfactants can be classified into four main categories: anionic, cationic, nonionic, and amphoteric, each with distinct properties and solubility characteristics.
Recommended video:
Liquid Chemicals: Surface-Active Agents
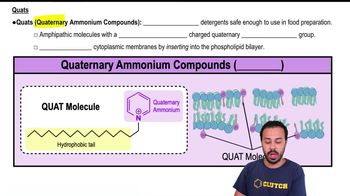
Cationic Surfactants
Cationic surfactants, such as quaternary ammonium compounds, carry a positive charge and are known for their antimicrobial properties. They are highly soluble in water and are often used in disinfectants and fabric softeners. Their solubility in water makes them effective in various applications, particularly in cleaning and sanitizing.
Recommended video:
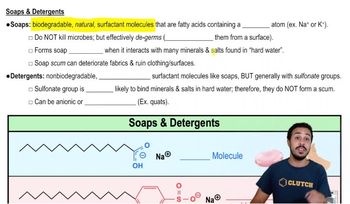
Soaps
Soaps are a type of anionic surfactant formed from the saponification of fats and oils. They consist of long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylate group that interacts with water, allowing them to emulsify oils and dirt. While soaps are effective in water, their solubility can be affected by the presence of hard water ions, which can precipitate them out of solution.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: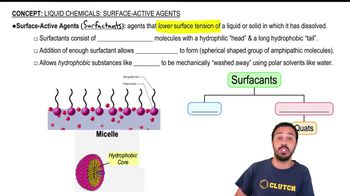

 2:29m
2:29m