Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
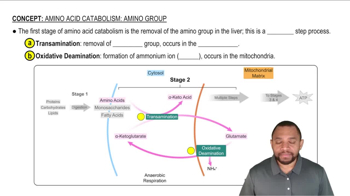
Amino Acid Catabolism
Amino acid catabolism refers to the metabolic process where amino acids are broken down to produce energy or convert into other compounds. This process involves deamination, where the amino group is removed, allowing the remaining carbon skeleton to enter various metabolic pathways, ultimately leading to the production of key metabolites like glucose, acetyl-CoA, and ketone bodies.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Concept 1
Ketone Bodies
Ketone bodies are water-soluble molecules produced in the liver from fatty acids and, to a lesser extent, from the breakdown of certain amino acids during periods of low carbohydrate availability. In amino acid catabolism, specific amino acids can be converted into acetoacetate, which can then be further transformed into ketone bodies, serving as an alternative energy source for tissues, especially during fasting or prolonged exercise.
Recommended video:
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA is a central metabolite in energy metabolism, formed from the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and certain amino acids. During amino acid catabolism, the carbon skeletons of ketogenic amino acids can be converted directly into acetyl-CoA, which then enters the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to produce ATP, or can be used for fatty acid synthesis, linking amino acid metabolism to energy production and storage.
Recommended video:
Phase B - Succinyl CoA Formation Example 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance