Textbook Question
Define what an “essential” nutrient is and explain how it differs from a “nonessential” nutrient.
30
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
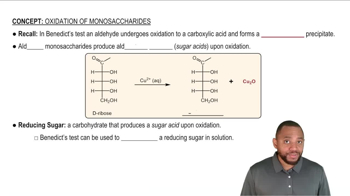


Define what an “essential” nutrient is and explain how it differs from a “nonessential” nutrient.
What citric acid cycle intermediates are precursors to amino acids?
What is the structure of the α-keto acid formed from transamination of the following amino acids?
a. Glutamic acid
Write the structure of the α-keto acid produced by oxidative deamination of the following amino acids (Refer to Table 18.3):
a. Leucine
What other product is formed in oxidative deamination besides an α-keto acid?
What is the structure of the α-keto acid formed by transamination of the amino acid phenylalanine (Phe)? Refer to Table 18.3 for the structure of Phe.