Can an amino acid be both glucogenic and ketogenic? Explain why or why not.
Determine how many ATPs you would make if you consumed a tetrapeptide comprised of leucine, histidine, valine, and lysine. Have each member of your group take one of the four amino acids and determine the number of ATPs their amino acid would make and combine them to get the total.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
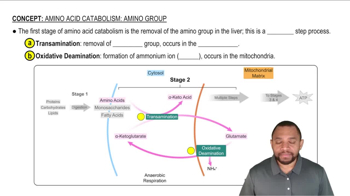
Amino Acid Catabolism
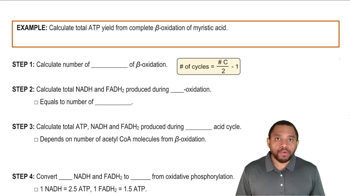
ATP Yield from Amino Acids
Metabolic Pathways

The pancreatic proteases are synthesized and stored as zymogens. They are activated after the pancreatic juices enter the small intestine. Why is it essential that these enzymes be synthesized and stored in their inactive forms?
Why might it be a bad idea to take large quantities of a single amino acid dietary supplement?
Unlike most amino acids, branched-chain amino acids are broken down in tissues other than the liver. Using Table 18.3, identify the three amino acids with branched-chain R groups. For any one of these amino acids, write the equation for its transamination.
Fumarate from step 3 of the urea cycle may be recycled into aspartate for use in step 2 of the cycle. The sequence of reactions for this process is
a. <IMAGE>
b. <IMAGE>
c. <IMAGE>
Classify each reaction as one of the following:
1. Oxidation
2. Reduction
3. Transamination
4. Elimination
5. Addition
In the liver, the relative activity of ornithine transcarbamylase is high, that of argininosuccinate synthetase is low, and that of arginase is high. Why is it important that ornithine transcarbamylase activity be high in the liver? What might be the consequence if arginase activity is low or defective?
