Textbook Question
Why does the body convert NH₄⁺ to urea for excretion?
22
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
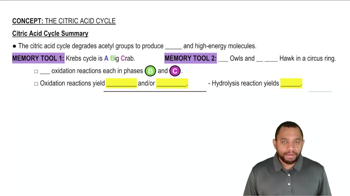


Why does the body convert NH₄⁺ to urea for excretion?
If you were diagnosed as having a diet low in lysine, what foods might you include in your diet to alleviate this problem?
Diet soft drinks that are sweetened with aspartame carry a warning label for phenylketonurics. Why?
Can an amino acid be both glucogenic and ketogenic? Explain why or why not.
The pancreatic proteases are synthesized and stored as zymogens. They are activated after the pancreatic juices enter the small intestine. Why is it essential that these enzymes be synthesized and stored in their inactive forms?
Why might it be a bad idea to take large quantities of a single amino acid dietary supplement?