Cholesterol (see structure below) and cholate (a bile acid anion, whose structure is shown on p. 731) are sterols with very similar structures. However, the roles they play in the body are different: Cholate is an emulsifier, whereas cholesterol plays an important role in membrane structure. Identify the small differences in their structures that make them well suited to their jobs in the body. Given their similar structures, can the roles of these molecules be reversed? <IMAGE>
Ch.24 Lipid Metabolism
Chapter 24, Problem 24.12
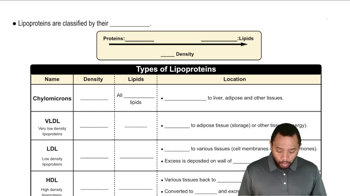
Identify each lipoprotein described here as either chylomicron, HDL, LDL, or VLDL.
d. Which lipoprotein contains “bad cholesterol” from a vascular disease risk standpoint?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the role of each type of lipoprotein in the body. Chylomicrons are responsible for transporting dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body. HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) is known as 'good cholesterol' because it helps remove cholesterol from the bloodstream. LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) is often referred to as 'bad cholesterol' because high levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries and result in vascular diseases. VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein) primarily carries triglycerides and can also contribute to plaque buildup.
Identify the lipoprotein associated with 'bad cholesterol'. From the descriptions, LDL is the lipoprotein that is commonly associated with 'bad cholesterol' due to its role in transporting cholesterol to tissues, which can lead to plaque formation in arteries.
Consider the health implications of high levels of LDL. Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol are linked to an increased risk of atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of fatty deposits in the walls of arteries, potentially leading to cardiovascular diseases.
Reflect on the importance of managing cholesterol levels. Maintaining a healthy balance between LDL and HDL is crucial for cardiovascular health. Lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and medication can help manage cholesterol levels.
Summarize the identification: The lipoprotein that contains 'bad cholesterol' from a vascular disease risk standpoint is LDL.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lipoproteins
Lipoproteins are complexes of lipids and proteins that transport fats through the bloodstream. They vary in density and composition, influencing their function and role in health. The main types include chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, and HDL, each serving distinct purposes in lipid metabolism and cardiovascular health.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Lipoproteins for Transport Concept 2
LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)
LDL, or Low-Density Lipoprotein, is often referred to as 'bad cholesterol' because high levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. It carries cholesterol from the liver to the cells, but when present in excess, it can contribute to atherosclerosis and other vascular issues.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lipoproteins for Transport Concept 2
Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Risk
Cholesterol is a waxy substance essential for various bodily functions, but its levels must be balanced. High levels of LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke, while HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) is considered 'good cholesterol' as it helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, thus reducing cardiovascular risk.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Steroids Example 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
26
views
Textbook Question
Oxygen is not a reactant in the ß oxidation of fatty acids. Can ß oxidation occur under anaerobic conditions? Explain.
41
views
Textbook Question
Identify each lipoprotein described here as either chylomicron, HDL, LDL, or VLDL.
a. Which lipoprotein has the lowest density? Why?
35
views
Textbook Question
One strategy used in many different biochemical pathways is an initial investment of energy early on and a large payoff in energy at the end of the pathway. How is this strategy utilized in the catabolism of fats?
5
views
Textbook Question
Compare the differences between ß oxidation and fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis). Are these pathways the reverse of each other?
24
views
Textbook Question
Why do lipids make you feel full for a long time after a meal?
12
views
