Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cerebrosides
Cerebrosides are a type of glycosphingolipid that consist of a sphingosine backbone, a fatty acid, and a single sugar residue. They play crucial roles in cell membrane structure and function, particularly in the nervous system. The sugar component can vary, with d-galactose being a common example, contributing to the molecule's identity and function.
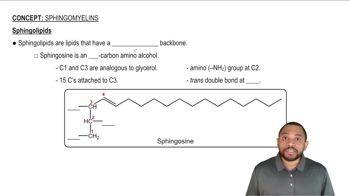
Sphingosine
Sphingosine is an amino alcohol that serves as the backbone for sphingolipids, including cerebrosides. It consists of a long hydrocarbon chain with an amine group and a hydroxyl group, allowing it to form various lipid structures. Sphingosine's unique structure contributes to the stability and functionality of cell membranes.
Recommended video:
Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid group at one end, and they are key components of lipids. In the context of cerebrosides, myristic acid, a saturated fatty acid with 14 carbon atoms, is esterified to the sphingosine backbone. The fatty acid influences the physical properties of the lipid, such as fluidity and membrane interactions.
Recommended video: