Draw the structure of a glycerophospholipid that contains palmitic acid, oleic acid, and the phosphate bonded to propanolamine.
Based on the information in Section 23.7, how would you expect each of these common metabolites to cross the cell membrane?
c. Ca2+
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Cell Membrane Structure

Transport Mechanisms
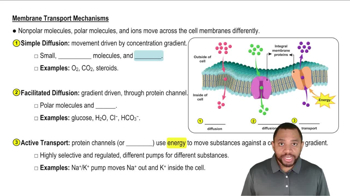
Ion Channels and Pumps

Cardiolipin, a compound found in heart muscle, has the following structure. What products are formed if all ester bonds in the molecule are saponified by treatment with aqueous NaOH? <IMAGE>
Which process requires energy—passive or active transport? Why is energy sometimes required to move solute across the cell membrane?
Based on the information in Section 23.7, how would you expect each of these common metabolites to cross the cell membrane?
a. NO (nitrous oxide)
Based on the information in Section 23.7, how would you expect each of these common metabolites to cross the cell membrane?
a. CO
Which of the following are saponifiable lipids? (Recall that ester bonds are broken by base hydrolysis.)
a. Progesterone
b. Glyceryl trioleate
c. A sphingomyelin
d. Prostaglandin E1
e. A cerebroside
f. A lecithin
