Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is the metabolic pathway through which organisms synthesize glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors, such as lactate, glycerol, and certain amino acids. This process primarily occurs in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys. It is crucial for maintaining blood glucose levels during fasting or intense exercise when glucose reserves are low.
Recommended video:
Gluconeogenesis Example 2
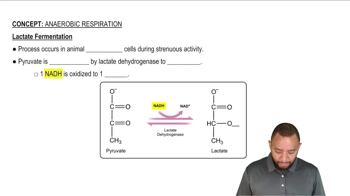
Lactate
Lactate is a byproduct of anaerobic metabolism, particularly during intense exercise when oxygen levels are insufficient for aerobic respiration. It can be converted back into glucose through gluconeogenesis, allowing the body to recycle energy and maintain glucose homeostasis. This conversion is especially important in the Cori cycle, where lactate produced in muscles is transported to the liver for glucose synthesis.
Recommended video:
Anaerobic Respiration Concept 3
Cori Cycle
The Cori cycle is a metabolic pathway that describes the conversion of lactate produced in muscles during anaerobic respiration back into glucose in the liver. This cycle helps to clear lactate from the bloodstream and provides a continuous supply of glucose for energy, especially during prolonged exercise. It illustrates the interconnectedness of muscle and liver metabolism in maintaining energy balance.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance