Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
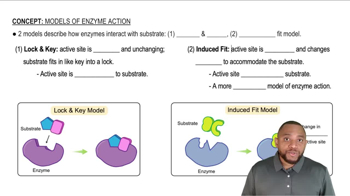
Induced-Fit Model
The induced-fit model describes how an enzyme changes shape upon substrate binding, allowing for a more precise fit. This flexibility enhances the enzyme's ability to catalyze reactions, as the active site adapts to the substrate's shape, improving the interaction and efficiency of the reaction.
Recommended video:
Models of Enzyme Action Concept 1
Lock-and-Key Model
The lock-and-key model suggests that enzymes and substrates fit together perfectly, like a key in a lock. While this model illustrates the specificity of enzyme-substrate interactions, it does not account for the dynamic nature of enzymes and their ability to undergo conformational changes during catalysis.
Recommended video:
Models of Enzyme Action Example 1
Enzyme Catalysis
Enzyme catalysis refers to the process by which enzymes accelerate chemical reactions. Understanding this concept is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of different models, as it highlights the importance of enzyme structure and flexibility in facilitating substrate conversion into products.
Recommended video:
Intro to Enzymes Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance