Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Feedback Inhibition
Feedback inhibition is a regulatory mechanism in metabolic pathways where the accumulation of an end product inhibits an earlier step in the pathway. This prevents the overproduction of the product and helps maintain homeostasis within the cell. In the context of the question, the buildup of pyruvate would signal the first enzyme to slow down or stop its activity, thereby regulating the flow of glucose conversion.
Recommended video:
Feedback Control Example 1
Enzyme Kinetics
Enzyme kinetics refers to the study of the rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions and how they change in response to various factors, including substrate concentration and the presence of inhibitors. Understanding enzyme kinetics is crucial for analyzing how enzymes respond to changes in product levels, as it provides insight into how feedback mechanisms can alter reaction rates and overall metabolic flow.
Recommended video:
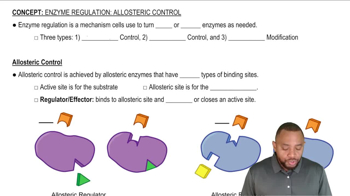
Allosteric Regulation
Allosteric regulation involves the binding of regulatory molecules to an enzyme at sites other than the active site, leading to conformational changes that affect enzyme activity. This type of regulation can enhance or inhibit enzyme function, allowing for fine-tuned control of metabolic pathways. In the scenario presented, the accumulation of the product may act as an allosteric inhibitor, affecting the first enzyme's activity in the glucose to pyruvate conversion pathway.
Recommended video:
Allosteric Control Concept 1