Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
<IMAGE>
a. The enzyme involved in this reaction belongs to what class of enzymes?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


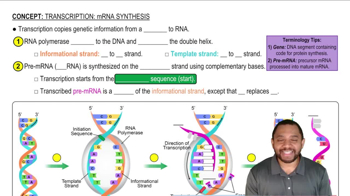
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
<IMAGE>
a. The enzyme involved in this reaction belongs to what class of enzymes?
Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(a) increasing the substrate concentration at a constant inhibitor concentration
Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(b) decreasing the inhibitor concentration at a constant substrate concentration.
What type of enzyme regulation occurs in the following situations?
d. Conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate is inhibited by high levels of ATP. (Hint: ATP is neither a product nor a substrate in this reaction.)
What general kinds of reactions do the following types of enzymes catalyze?
b. Decarboxylases
What general kinds of reactions do the following types of enzymes catalyze?
c. Lipases