Open Question
Indicate whether each of the following molecules is an α-amino acid or not, and explain why.
a. <IMAGE>
78
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

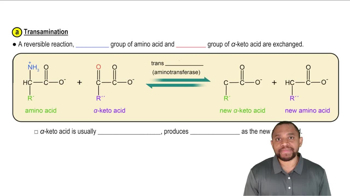
Indicate whether each of the following molecules is an α-amino acid or not, and explain why.
a. <IMAGE>
Proteins are usually least soluble in water at their isoelectric points. Explain.
How could you make the zwitterion of aspartic acid more soluble in water?
What is the sequence of atoms along the 'backbone' of a protein?
Bradykinin, a peptide that helps to regulate blood pressure, has the primary structure Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg.
b. Bradykinin has a very kinked secondary structure. Why?
Bradykinin, a peptide that helps to regulate blood pressure, has the primary structure Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg.
a. Draw the complete structural formula of bradykinin.