Give names or structures for the following ammonium salts. Indicate whether each is the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
a. <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

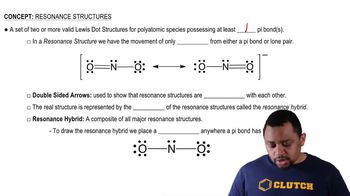

Give names or structures for the following ammonium salts. Indicate whether each is the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
a. <IMAGE>
Give names or structures for the following ammonium salts. Indicate whether each is the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
a. <IMAGE>
Draw the structures of the ammonium ions formed when the amines in Problem 16.30 are treated with acid.
Complete the following equations. (Hint: Remember that a nitrogen with three groups bound to it has a lone pair and one with four does not; see Worked Examples 16.4 and 16.5 for help.)
a. <IMAGE>
Choline has the following structure. Do you think that this substance reacts with aqueous hydrochloric acid? If so, what is the product? If not, why not? <IMAGE>
Name the following compounds:
a. <IMAGE>