Textbook Question
Name the following compounds:
a. <IMAGE>
127
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

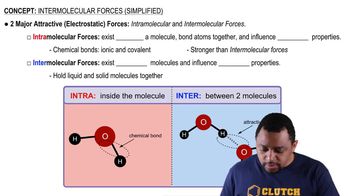

Name the following compounds:
a. <IMAGE>
Complete the following equations (Hint: Answers may include concepts learned from previous organic chapters):
e. <IMAGE>
Draw the condensed and line formula of the molecule in the margin. Is it a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine? Why?
<IMAGE>
Provide compounds that fit the following descriptions:
a. Two amines that are gases at room temperature
b. A heterocyclic amine
c. A compound with an amine group on an aromatic ring
Give names or structures for the following ammonium salts. Indicate whether each is the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
c. N-Butyl-N-isopropylhexylammonium chloride