Textbook Question
What are the names of these amines?
a. (CH₃CH₂CH₂)₂NH
221
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
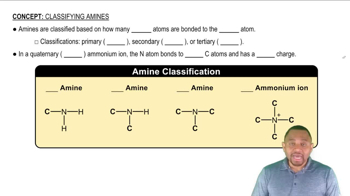


What are the names of these amines?
a. (CH₃CH₂CH₂)₂NH
What are the names of these amines?
c. <IMAGE>
Write the structure of benzylamine hydrochloride in two different ways, and name the hydrochloride as an ammonium salt.
<IMAGE>
The structure of the amino acid lysine (in its uncharged form) is shown below.
<IMAGE>
b. Is lysine likely to be water-soluble? Explain.
Explain what bonds must be made or broken and where the electrons go when the hydrogen-bonded water between the two amines shown on page 507 reacts to form an amine, ammonium ion, and OH⁻.
Complete the following equations:
b. <IMAGE>