Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation of Alcohols
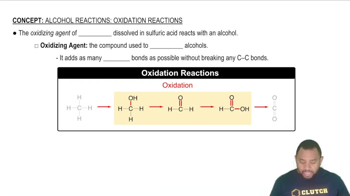
Oxidation of alcohols involves the conversion of alcohols into carbonyl compounds, such as aldehydes or ketones, and ultimately to carboxylic acids, depending on the type of alcohol and the oxidizing agent used. Primary alcohols typically oxidize to aldehydes, while secondary alcohols convert to ketones. Tertiary alcohols do not oxidize easily due to the lack of a hydrogen atom on the carbon bearing the hydroxyl group.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Oxidation Concept 1
Types of Alcohols
Alcohols are classified into three categories: primary, secondary, and tertiary, based on the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon bearing the hydroxyl (-OH) group. Primary alcohols have one carbon attached, secondary alcohols have two, and tertiary alcohols have three. This classification affects their reactivity and the products formed during oxidation.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Classification Concept 2
Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing agents are substances that facilitate the oxidation of other compounds by accepting electrons. Common oxidizing agents for alcohols include potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) and chromium trioxide (CrO3), which can convert alcohols into their corresponding carbonyl compounds. The choice of oxidizing agent can influence the reaction pathway and the final products obtained.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Oxidation Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance