Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enthalpy Change (∆H)
Enthalpy change (∆H) refers to the heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction or phase change at constant pressure. In this context, the positive value of ∆H for the transition from liquid to gas indicates that the process is endothermic, meaning it requires energy input. For the reverse process, from gas to liquid, ∆H will be negative, reflecting the release of energy.
Recommended video:
Physical & Chemical Changes
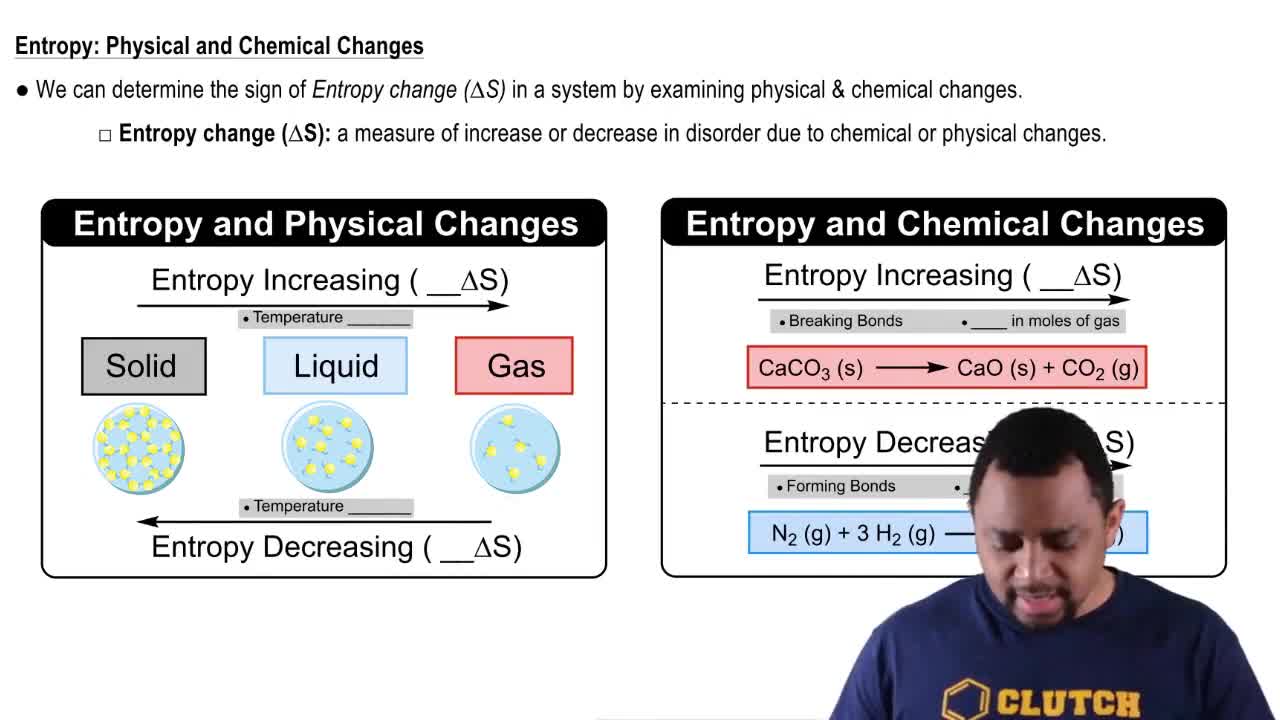
Entropy Change (∆S)
Entropy change (∆S) measures the degree of disorder or randomness in a system. A negative value of ∆S, as seen in the transition from liquid to gas, indicates a decrease in disorder, as gas molecules are more dispersed than liquid molecules. Conversely, when transitioning from gas to liquid, ∆S will be positive, signifying an increase in order as the gas condenses into a liquid.
Recommended video:
Entropy (Simplified) Concept 2
Thermodynamic Relationships
Thermodynamic relationships, particularly the Gibbs free energy equation (∆G = ∆H - T∆S), help predict the spontaneity of a process. In this case, understanding how ∆H and ∆S change during phase transitions is crucial for calculating the values for the reverse process. The temperature (T) plays a significant role in determining the overall energy changes and spontaneity of the phase change.
Recommended video:
First Law of Thermodynamics
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance