Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molar Mass of Water
The molar mass of water (H2O) is approximately 18 g/mol. This value is essential for converting grams of water to moles, which is necessary for calculating the energy released during the phase change from liquid to solid.
Recommended video:
Phase Change and Latent Heat
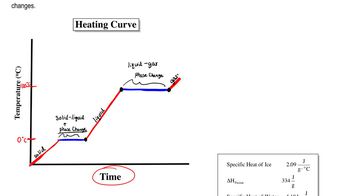
Phase change refers to the transition of a substance from one state of matter to another, such as from liquid to solid. The latent heat of fusion for water is the amount of energy released when water freezes, quantified as 1.44 kcal/mol, which is crucial for determining the total energy released when a specific mass of water freezes.
Recommended video:
Energy Calculation
To find the total energy released during the freezing of water, one must calculate the number of moles in the given mass and then multiply by the latent heat of fusion. This involves using the formula: Energy = moles × latent heat, which provides the total energy in kilocalories for the specified mass of water.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance