Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molarity
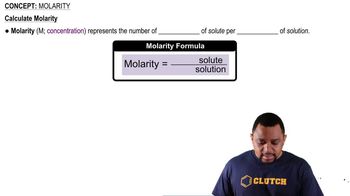
Molarity is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is calculated using the formula M = moles of solute / liters of solution. In this case, to find the molarity of citric acid, one must first convert the mass of citric acid into moles using its molar mass, then divide by the volume of the solution in liters.
Recommended video:
Normality
Normality is another measure of concentration that reflects the number of equivalents of a solute per liter of solution. For acids, normality is particularly relevant as it accounts for the number of protons (H⁺ ions) that can be donated. Since citric acid is triprotic, it can donate three protons, meaning its normality will be three times its molarity when calculating the solution's concentration.
Recommended video:
Triprotic Acid
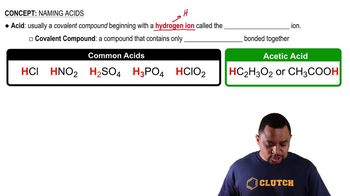
A triprotic acid is an acid that can donate three protons (H⁺ ions) per molecule in a reaction. Citric acid (C₆H₅O₇H₃) is an example of a triprotic acid, which means that when calculating its normality, one must consider the total number of protons available for reaction. This characteristic is essential for determining the solution's acidity and its behavior in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance