Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
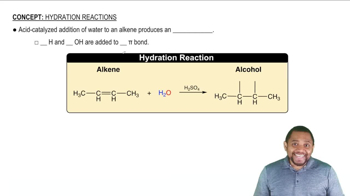
Hydration Reactions
Hydration reactions involve the addition of water to a compound, typically an alkene, resulting in the formation of alcohols. This process is crucial in organic chemistry as it transforms unsaturated hydrocarbons into more functionalized products. Understanding the mechanism of hydration, including the role of catalysts like acids, is essential for predicting the products of these reactions.
Recommended video:
Symmetric Alkene Hydration Concept 1
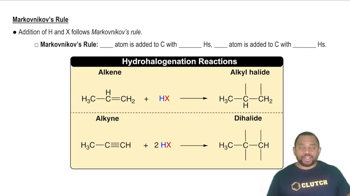
Markovnikov's Rule
Markovnikov's Rule states that in the addition of HX (where X is a halogen or OH) to an alkene, the hydrogen atom will attach to the carbon with the greater number of hydrogen atoms already attached. This principle helps predict the major product of hydration reactions, guiding chemists in determining the structure of the resulting alcohol based on the alkene's substitution pattern.
Recommended video:
Markovnikov's Rule Concept 2
Reaction Mechanism
A reaction mechanism outlines the step-by-step sequence of elementary reactions that occur during a chemical transformation. In hydration reactions, understanding the mechanism helps in identifying intermediates, such as carbocations, and the transition states involved. This knowledge is vital for predicting reaction outcomes and optimizing conditions for desired products.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance