Textbook Question
Identify each of the following as a purine or a pyrimidine:
a. guanine
5
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
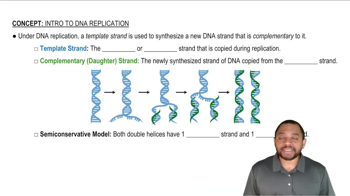
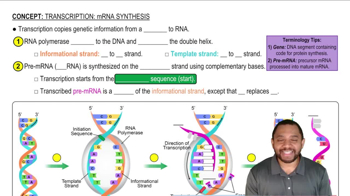
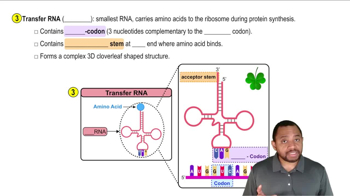
Identify each of the following as a purine or a pyrimidine:
a. guanine
The sequence of bases in a DNA template strand is 5'GGCTTATTGCCA3'. What is the corresponding mRNA produced?
Provide the three-letter amino acid sequence expected from each of the following mRNA segments: b. 5'UUU|CCC|UUU|CCC3'
Consider the following portion of mRNA produced by the normal order of DNA nucleotides: 5'CUU|AAA|CGA|GUU3' a. Write the amino acid sequence that would be produced from this mRNA.
For each of the following, note whether the component can be found in a virus, a cell, or both.
c. capsid
For each of the following, note whether the component can be found in a virus, a cell, or both.
a. RNA