Textbook Question
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
a. dTMP
8
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
a. dTMP
Identify the base and sugar in each of the following nucleotides:
d. GMP
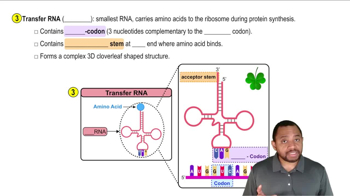
Match the following statements with mRNA, rRNA, or tRNA: a. combines with proteins to form ribosomes
List the possible codons for each of the following amino acids:
a. threonine
List the possible codons for each of the following amino acids:
a. valine
List the possible codons for each of the following amino acids:
c. histidine