In this video on Triacylglycerol reactions, we take a look at hydrogenation. Now, recall that under this type of reaction, we're going to have 2 hydrogens being added to 1 pi bond. And we say here that the conversion from double bonds to single bonds will help to decrease unsaturation as we lose our pi bonds, and this will cause an increase in melting point.
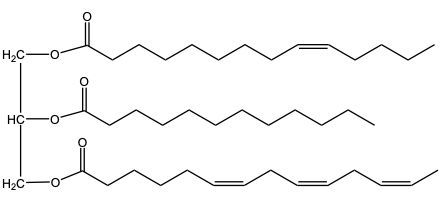
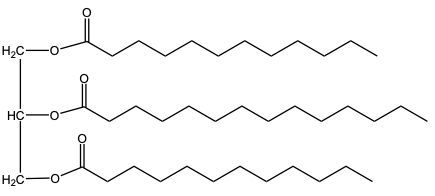
When we take a look at hydrogenation reactions, realize that there was complete hydrogenation where all of our carbon-carbon double bonds are reduced to single bonds. And then we also have partial hydrogenation when some, but not all carbon-carbon double bonds are reduced to single bonds. Now, if we take a look here at the complete one, we have here our triglyceride molecule or our Triacylglycerol molecule, and we're going to say here, triolein is its name. And here, if we look at our products, we can see that all 3 double bonds have been removed. And now we have just single bonded fatty acid chains.
Here remember when it comes to hydrogenation we use H 2 with some type of metal catalyst. Here, nickel is a common type of metal catalyst that is used. Also remember that when it comes to hydrogenation, 1 mole of H 2 is required for every single pi bond that we have. Because there are 3 Pi Bonds that were erased and are no longer part of my product, that means I used 3 moles of H 2 to do this complete hydrogenation.
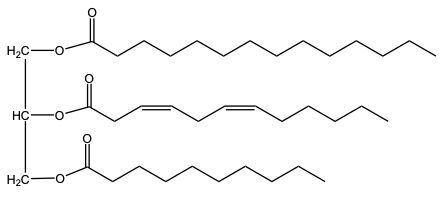
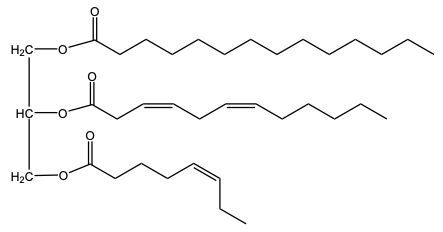
Now, again with partial hydrogenation, some but not all carbon double bonded carbon bonds are reduced to single bonds. Here, we start out with 3, and at the end, we only have one left. 2 of them were removed and reduced. So, since 2 pi bonds were removed, that would mean that we needed 2 moles of H 2 and we still use our Nickel catalyst.
Now, what's the whole point of doing partial hydrogenation? Why not go all the way and reduce all the pi bonds to single bonds? Well, we're going to say that this is commercially manufactured. We're going to say here that partial hydrogenation converts oils to different types of margarines. And ultimate consistency is based on the number of pi bonds. So companies will make these partially hydrogenated oils in order to make different types of margarines; we can actually affect the hardness of these margarines because there are soft margarines versus hard margarines based on the number of pi bonds remaining in our product.
Alright. So normally we do complete hydrogenation, but some companies are able to only do partial hydrogenation where they want to create margarines from oils. Alright. So just keep this in mind, hydrogenation, that it can be complete or it can be partial.