- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

What is the line structure and condensed formula for the following amine?
Is it classified as tertiary, secondary, or primary? Why?
Provide the correct name of the following amine: (CH3CH2CH2CH2)2NH
Consider the ammonium salt shown below. Provide its name and identify if it is a salt of primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.

Is the following amine soluble in water? Why or why not?
The zwitterion structure of leucine (pI = 6.0) is shown below. Draw the predominant structure of leucine at pH 2.0 and determine its net charge.
What are the names and three-letter abbreviations of polar amino acids that contain an amide in their side chains?
Which amino acid is represented by the letter C? Draw its structure ignoring stereochemistry.
Which of the following statements about the polarity of the R groups, their respective acidity or basicity, and hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity are correct?
I) Amino acids with nonpolar, aliphatic R groups are generally hydrophobic and do not significantly affect the acidity or basicity of the amino acid.
II) Amino acids with polar, uncharged R groups are hydrophilic and can participate in hydrogen bonding, but they do not influence the overall charge of the amino acid.
III) Amino acids with acidic R groups are hydrophobic due to their negative charge, which repels water molecules.
IV) Amino acids with basic R groups are generally hydrophilic and positively charged, making them soluble in water.
V) Aromatic amino acids with hydrophobic rings are always neutral in terms of charge and do not participate in hydrogen bonding.
Provide the products of the condensation reaction shown below. (Assume that they bond in the order shown.)
Consider the following protein chain:

How many amino acids make the atoms in a planar unit? Why are the units planar?
True or False: Globular proteins, unlike fibrous proteins, are water-insoluble and composed of compact, non-repeating structures.
If all serine is replaced with leucine in a protein, what would you expect from the protein's tertiary structure?
Which of the following shows a protein with a quaternary structure and the correct number of polypeptides that make up that protein?
Given the following amino acids (His, Tyr, Trp, and Thr) in a protein, which of these have R groups that could exhibit salt bridges? (Select all that apply.)
I. His
II. Tyr
III. Trp
IV. Thr
The hydrolysis of isomaltose results in the formation of two glucose molecules with isomaltase as the enzyme. Construct an energy diagram illustrating the hydrolysis reaction progression with and without the presence of isomaltase.
Consider the following reaction:
Identify the subclass of oxidoreductase enzyme that facilitates this reaction.
True or false: An enzyme has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate.
Why is it said that enzymatic reactions follow an 'induced fit' rather than 'lock and key' mechanism?
Amylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch into sugars in the human mouth and pancreas. Its optimal activity is at a pH of 6.7 to 7.0. What would be the effect on the rate of an amylase-catalyzed reaction if the pH was adjusted to 4.5?
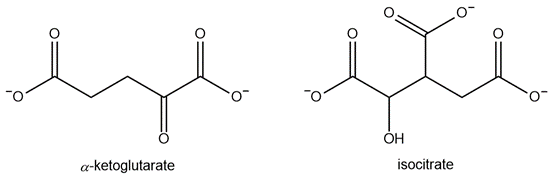
During a biochemical experiment, it was found that α-ketoglutarate acts as an inhibitor of isocitrate dehydrogenase.
Would α-ketoglutarate act as a competitive or noncompetitive inhibitor?
Identify the type of enzyme regulation in the scenario below:
The conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate, catalyzed by pyruvate kinase, is inhibited by high concentrations of alanine. Note that in this reaction, alanine is neither a product nor a substrate.
What type of enzyme regulation is being described in the following scenario?
The accumulation of ATP, a product of cellular respiration, inhibits the first enzyme in the process that breaks down glucose.
Which of the statements below best describes how enzyme activity is regulated by genetic control?
Xylulose is a rare sugar that participates in cellular carbohydrate metabolism. Determine the classification of this monosaccharide as an aldopentose, ketopentose, aldohexose, or ketohexose.
Which of the following important monosaccharides is correctly paired with its natural source?
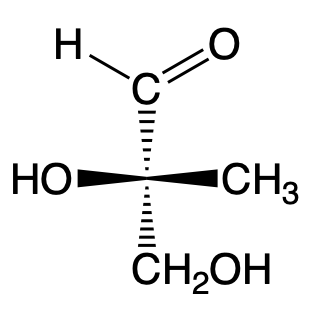
Give the appropriate Fischer projection for the wedge-dash structure shown below: