- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

How do enzymes facilitate chemical reactions in the human body?
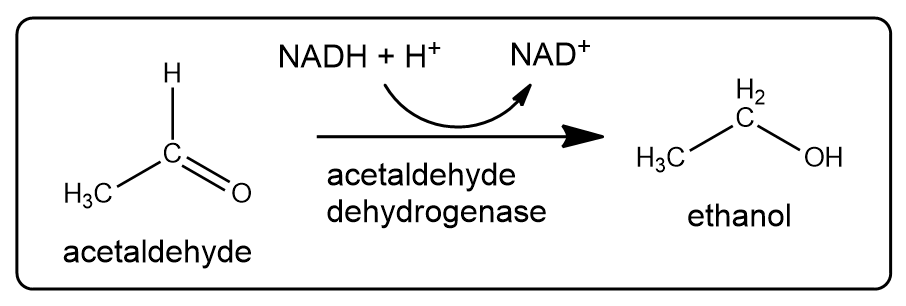
What is the product in the following reaction as written?
Identify the substrate and product and describe the chemical change in the dehydrogenase-catalyzed reaction involving acetaldehyde and ethanol.
People with celiac disease cannot properly digest gluten found in wheat. A supplement called GlutenEase claims to help digest gluten-containing foods. What enzyme is likely to be present in GlutenEase, and what is the major class of this enzyme?
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about the enzyme-substrate complex?
(i) It is the final product of the enzymatic reaction.
(ii) It is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
(iii) It is a permanent bond formed between an enzyme and the substrate.
What type of interaction will most likely stabilize an enzyme-substrate (ES) complex involving a substrate with a large nonpolar region?
Explain using the lock-and-key model why pepsin can hydrolyze peptide bonds in proteins but not the glycosidic bonds in starch.
Which of the following statements are true regarding the active site, lock-and-key model, and induced-fit model of enzymes?
I. The active site of an enzyme is a rigid structure that perfectly fits the substrate in the lock-and-key model.
II. The induced-fit model suggests that the enzyme's active site undergoes a conformational change upon substrate binding to better fit the substrate.
III. The lock-and-key model accounts for the enzyme’s ability to adapt its structure to different substrates.
IV. In the induced-fit model, the enzyme’s active site is rigid and does not change shape during substrate binding.
What would be the likely impact on the rate of a biochemical reaction catalyzed by an enzyme that functions optimally at room temperature (about 25°C) if a reducing agent like dithiothreitol (DTT) is introduced?
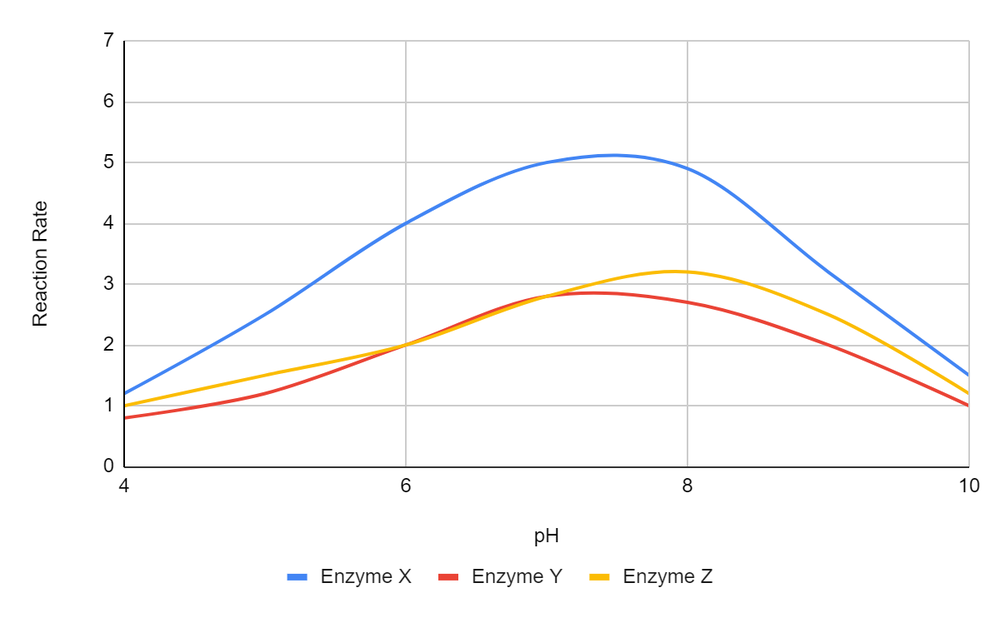
Using the provided graph, identify which of the following conditions is closest to the optimum reaction rate. Select the best answer.
Consider the three forms of enzyme inhibition (competitive, uncompetitive, and irreversible). Determine if the statement below is true or false. If false, correct the statement:
Each of the three kinds of inhibition involves the formation of covalent bonds with the enzyme.
Determine the type of inhibition the following scenario describes:
An inhibitor that does not resemble the substrate in structure is added, causing a decrease in the reaction rate and a conformational change in the enzyme.
Allosteric enzymes have two distinct binding sites. What is the purpose of each type of binding site?
What are the benefits of feedback inhibition in metabolic pathways?
Choose the appropriate type of enzymatic control for the scenarios given below:
a. An enzyme that is excessively active in the time of an infection
b. An enzyme required only when there is a high level of blood sugar
c. An enzyme that becomes active in response to a severe burn
d. An enzyme required only in the course of pregnancy