Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a vital coenzyme that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of fatty acids and the synthesis and oxidation of pyruvate. It is involved in the transfer of acyl groups, which are essential for various biochemical reactions. CoA is derived from pantothenic acid, also known as vitamin B5, highlighting its importance in energy production and metabolic pathways.
Recommended video:
Vitamins and Coenzymes
Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential for normal growth and nutrition, typically required in small quantities in the diet. Many vitamins serve as precursors to coenzymes, which are non-protein molecules that assist enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions. Understanding the relationship between vitamins and their corresponding coenzymes is crucial for grasping metabolic processes.
Recommended video:
Metabolic Pathways
Metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell that lead to the conversion of substrates into products. These pathways are essential for energy production, biosynthesis, and the regulation of cellular functions. Coenzymes like CoA are integral to these pathways, facilitating the transfer of chemical groups and enabling the efficient processing of nutrients.
Recommended video:
Metabolic Pathways Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution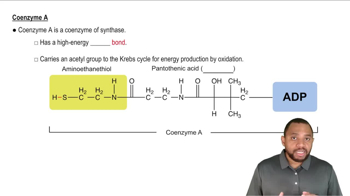



 2:23m
2:23m