Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Replication
Replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its DNA, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material. This occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle and involves enzymes like DNA polymerase, which synthesize new strands complementary to the original DNA template.
Recommended video:
Intro to DNA Replication Example 2
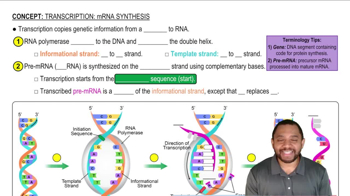
Transcription
Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template. During transcription, the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a specific region of the DNA and creates a single-stranded RNA molecule that carries the genetic information needed for protein synthesis. This process occurs in the nucleus in eukaryotic cells.
Recommended video:
Transcription: mRNA Synthesis Concept 1
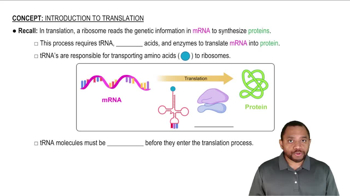
Translation
Translation is the process by which the information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide chain, forming a protein. This occurs in the ribosome, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring specific amino acids that correspond to the codons in the mRNA sequence, ultimately leading to protein synthesis.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Translation Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 1:42m
1:42m