Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aldehyde Functional Group
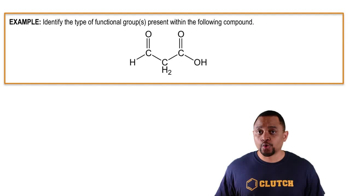
An aldehyde is characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of a carbon chain. The general formula for aldehydes is R-CHO, where R represents a hydrocarbon group. In the given compound, CH3CH2―O―CH2―CHO, the terminal -CHO indicates the presence of an aldehyde functional group.
Recommended video:
Functional Group Priorities Concept 1
Ketone Functional Group
A ketone features a carbonyl group (C=O) located within a carbon chain, specifically between two carbon atoms. The general formula for ketones is R1-CO-R2, where R1 and R2 are hydrocarbon groups. In the provided compound, there is no ketone present, as the carbonyl group is at the end of the chain, classifying it as an aldehyde.
Recommended video:
Functional Group Priorities Concept 1
Carbonyl Group
The carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O). It is a key feature in both aldehydes and ketones, influencing their chemical properties and reactivity. Understanding the structure and behavior of the carbonyl group is essential for identifying compounds containing aldehyde or ketone functionalities.
Recommended video:
Functional Groups with Carbonyls Example 3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 2:38m
2:38m