Table of contents
- 1. Matter and Measurements4h 29m
- What is Chemistry?7m
- The Scientific Method9m
- Classification of Matter16m
- States of Matter8m
- Physical & Chemical Changes19m
- Chemical Properties8m
- Physical Properties5m
- Intensive vs. Extensive Properties13m
- Temperature (Simplified)9m
- Scientific Notation13m
- SI Units (Simplified)5m
- Metric Prefixes24m
- Significant Figures (Simplified)11m
- Significant Figures: Precision in Measurements7m
- Significant Figures: In Calculations19m
- Conversion Factors (Simplified)15m
- Dimensional Analysis22m
- Density12m
- Specific Gravity9m
- Density of Geometric Objects19m
- Density of Non-Geometric Objects8m
- 2. Atoms and the Periodic Table5h 22m
- The Atom (Simplified)9m
- Subatomic Particles (Simplified)12m
- Isotopes17m
- Ions (Simplified)22m
- Atomic Mass (Simplified)18m
- Atomic Mass (Conceptual)12m
- Periodic Table: Element Symbols6m
- Periodic Table: Classifications11m
- Periodic Table: Group Names8m
- Periodic Table: Representative Elements & Transition Metals7m
- Periodic Table: Elemental Forms (Simplified)6m
- Periodic Table: Phases (Simplified)8m
- Law of Definite Proportions9m
- Atomic Theory9m
- Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment9m
- Wavelength and Frequency (Simplified)5m
- Electromagnetic Spectrum (Simplified)11m
- Bohr Model (Simplified)9m
- Emission Spectrum (Simplified)3m
- Electronic Structure4m
- Electronic Structure: Shells5m
- Electronic Structure: Subshells4m
- Electronic Structure: Orbitals11m
- Electronic Structure: Electron Spin3m
- Electronic Structure: Number of Electrons4m
- The Electron Configuration (Simplified)22m
- Electron Arrangements5m
- The Electron Configuration: Condensed4m
- The Electron Configuration: Exceptions (Simplified)12m
- Ions and the Octet Rule9m
- Ions and the Octet Rule (Simplified)8m
- Valence Electrons of Elements (Simplified)5m
- Lewis Dot Symbols (Simplified)7m
- Periodic Trend: Metallic Character4m
- Periodic Trend: Atomic Radius (Simplified)7m
- 3. Ionic Compounds2h 20m
- Periodic Table: Main Group Element Charges14m
- Periodic Table: Transition Metal Charges5m
- Periodic Trend: Ionic Radius (Simplified)5m
- Periodic Trend: Ranking Ionic Radii8m
- Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy (Simplified)9m
- Periodic Trend: Electron Affinity (Simplified)8m
- Ionic Bonding6m
- Naming Monoatomic Cations6m
- Naming Monoatomic Anions5m
- Polyatomic Ions25m
- Naming Ionic Compounds11m
- Writing Formula Units of Ionic Compounds7m
- Naming Ionic Hydrates6m
- Naming Acids18m
- 4. Molecular Compounds2h 18m
- Covalent Bonds6m
- Naming Binary Molecular Compounds6m
- Molecular Models4m
- Bonding Preferences6m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds (Simplified)8m
- Multiple Bonds4m
- Multiple Bonds (Simplified)6m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Multiple Bonds10m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Ions (Simplified)8m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Exceptions (Simplified)12m
- Resonance Structures (Simplified)5m
- Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (Simplified)4m
- Electron Geometry (Simplified)8m
- Molecular Geometry (Simplified)11m
- Bond Angles (Simplified)11m
- Dipole Moment (Simplified)15m
- Molecular Polarity (Simplified)7m
- 5. Classification & Balancing of Chemical Reactions3h 17m
- Chemical Reaction: Chemical Change5m
- Law of Conservation of Mass5m
- Balancing Chemical Equations (Simplified)13m
- Solubility Rules16m
- Molecular Equations18m
- Types of Chemical Reactions12m
- Complete Ionic Equations18m
- Calculate Oxidation Numbers15m
- Redox Reactions17m
- Spontaneous Redox Reactions8m
- Balancing Redox Reactions: Acidic Solutions17m
- Balancing Redox Reactions: Basic Solutions17m
- Balancing Redox Reactions (Simplified)13m
- Galvanic Cell (Simplified)16m
- 6. Chemical Reactions & Quantities2h 34m
- 7. Energy, Rate and Equilibrium3h 45m
- Nature of Energy6m
- First Law of Thermodynamics7m
- Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions7m
- Bond Energy14m
- Thermochemical Equations12m
- Heat Capacity19m
- Thermal Equilibrium (Simplified)8m
- Hess's Law23m
- Rate of Reaction11m
- Energy Diagrams12m
- Rate Law (Simplified)5m
- Chemical Equilibrium7m
- The Equilibrium Constant14m
- Le Chatelier's Principle20m
- Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)17m
- Spontaneous vs Nonspontaneous Reactions7m
- Entropy (Simplified)9m
- Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified)18m
- 8. Gases, Liquids and Solids3h 27m
- Pressure Units6m
- Kinetic Molecular Theory14m
- The Ideal Gas Law18m
- The Ideal Gas Law Derivations13m
- The Ideal Gas Law Applications6m
- Chemistry Gas Laws17m
- Chemistry Gas Laws: Combined Gas Law12m
- Standard Temperature and Pressure14m
- Dalton's Law: Partial Pressure (Simplified)13m
- Gas Stoichiometry18m
- Intermolecular Forces (Simplified)19m
- Intermolecular Forces and Physical Properties11m
- Atomic, Ionic and Molecular Solids10m
- Heating and Cooling Curves30m
- 9. Solutions4h 27m
- Solutions6m
- Solubility and Intermolecular Forces17m
- Solutions: Mass Percent6m
- Percent Concentrations10m
- Molarity18m
- Osmolarity15m
- Parts per Million (ppm)13m
- Solubility: Temperature Effect8m
- Intro to Henry's Law4m
- Henry's Law Calculations12m
- Dilutions12m
- Solution Stoichiometry14m
- Electrolytes (Simplified)13m
- Equivalents11m
- Molality15m
- The Colligative Properties15m
- Boiling Point Elevation16m
- Freezing Point Depression9m
- Osmosis16m
- Osmotic Pressure10m
- Vapor Pressure Lowering (Raoult's Law)16m
- 10. Acids and Bases3h 10m
- Acid-Base Introduction11m
- Arrhenius Acid and Base6m
- Bronsted Lowry Acid and Base21m
- Acid and Base Strength17m
- Ka and Kb16m
- The pH Scale16m
- Auto-Ionization9m
- pH of Strong Acids and Bases9m
- Acid-Base Equivalents14m
- Acid-Base Reactions7m
- Gas Evolution Equations (Simplified)6m
- Ionic Salts (Simplified)11m
- Buffers11m
- Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation16m
- Strong Acid Strong Base Titrations (Simplified)13m
- 11. Nuclear Chemistry1h 1m
- BONUS: Lab Techniques and Procedures1h 38m
- BONUS: Mathematical Operations and Functions47m
- 12. Introduction to Organic Chemistry1h 34m
- 13. Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds2h 30m
- Spatial Orientation of Bonds3m
- Intro to Hydrocarbons16m
- Isomers14m
- Chirality15m
- Naming Alkenes11m
- Naming Dienes and Trienes6m
- Naming Alkynes9m
- Intro to Addition Reactions4m
- Halogenation Reaction4m
- Hydrogenation Reaction3m
- Hydrohalogenation Reaction7m
- Hydration Reaction10m
- Naming Benzene19m
- Benzene Reactions10m
- Benzene Reaction: Nitration6m
- Benzene Reaction: Sulfonation5m
- 14. Compounds with Oxygen or Sulfur1h 22m
- 15. Aldehydes and Ketones1h 1m
- 16. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives1h 11m
- 17. Amines40m
- 18. Amino Acids and Proteins2h 2m
- 19. Enzymes1h 37m
- 20. Carbohydrates1h 46m
- Intro to Carbohydrates4m
- Classification of Carbohydrates4m
- Fischer Projections4m
- Enantiomers vs Diastereomers7m
- D vs L Enantiomers9m
- Cyclic Hemiacetals8m
- Intro to Haworth Projections4m
- Cyclic Structures of Monosaccharides11m
- Mutarotation4m
- Reduction of Monosaccharides10m
- Oxidation of Monosaccharides7m
- Glycosidic Linkage14m
- Disaccharides7m
- Polysaccharides8m
- 21. The Generation of Biochemical Energy2h 9m
- 22. Carbohydrate Metabolism2h 31m
- 23. Lipids2h 26m
- Intro to Lipids6m
- Fatty Acids25m
- Physical Properties of Fatty Acids6m
- Waxes4m
- Triacylglycerols12m
- Triacylglycerol Reactions: Hydrogenation8m
- Triacylglycerol Reactions: Hydrolysis13m
- Triacylglycerol Reactions: Oxidation7m
- Glycerophospholipids15m
- Sphingomyelins13m
- Steroids15m
- Cell Membranes7m
- Membrane Transport10m
- 24. Lipid Metabolism1h 45m
- 25. Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism1h 37m
- 26. Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis2h 54m
- Intro to Nucleic Acids4m
- Nitrogenous Bases16m
- Nucleoside and Nucleotide Formation9m
- Naming Nucleosides and Nucleotides13m
- Phosphodiester Bond Formation7m
- Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids11m
- Base Pairing10m
- DNA Double Helix6m
- Intro to DNA Replication20m
- Steps of DNA Replication11m
- Types of RNA10m
- Overview of Protein Synthesis4m
- Transcription: mRNA Synthesis9m
- Processing of pre-mRNA5m
- The Genetic Code6m
- Introduction to Translation7m
- Translation: Protein Synthesis18m
22. Carbohydrate Metabolism
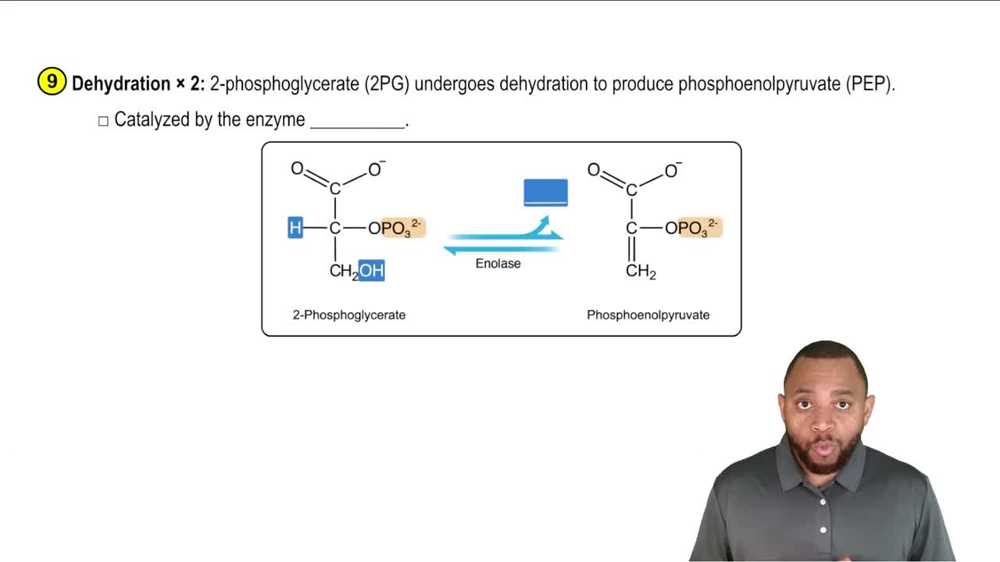
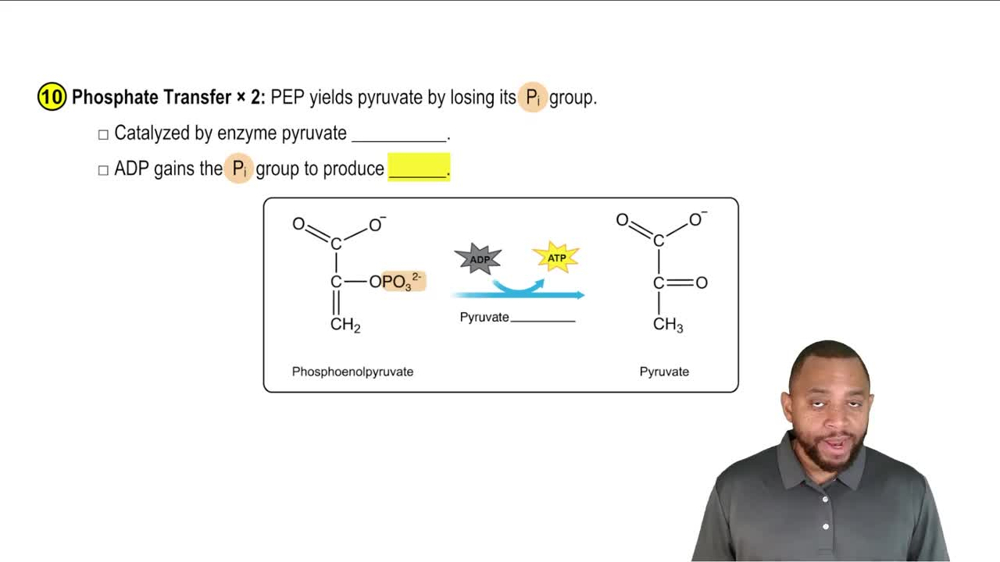
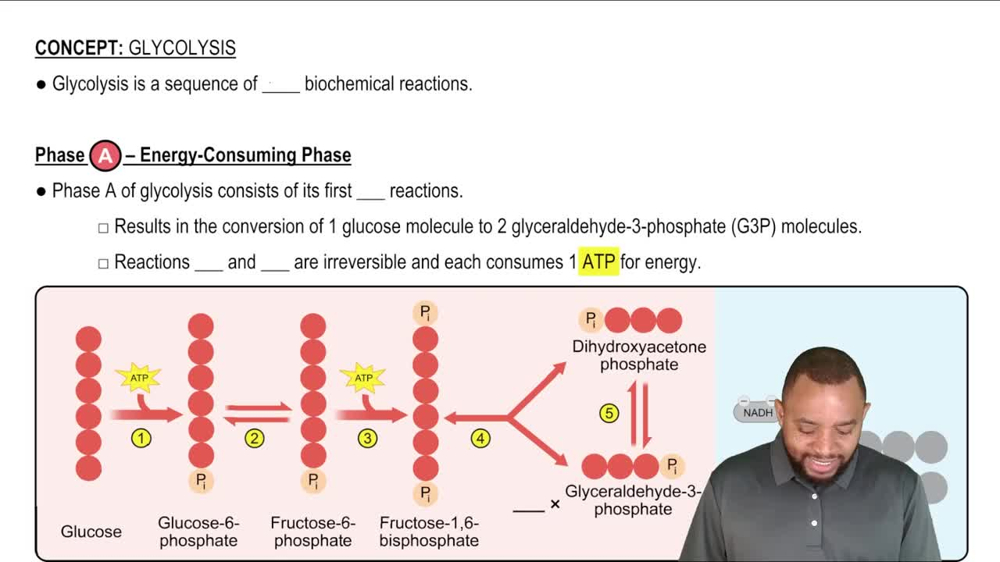
Glycolysis

Glycolysis Concept 2
Jules Bruno
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Related Videos
Related Practice