Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Pyruvate Decarboxylation
Pyruvate decarboxylation is the process by which pyruvate, produced from glycolysis, is converted into acetyl-CoA. This reaction occurs in the mitochondria and is catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Acetyl-CoA is a crucial substrate for the citric acid cycle, especially under aerobic conditions when oxygen is available.
Recommended video:
Pyruvate Oxidation Concept 2
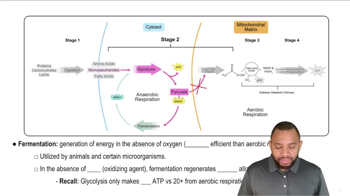
Fermentation
Fermentation is an anaerobic process that occurs when oxygen is scarce. In this pathway, pyruvate is converted into lactate in animals or ethanol and carbon dioxide in yeast. This process allows for the regeneration of NAD+, enabling glycolysis to continue producing ATP in the absence of oxygen.
Recommended video:
Anaerobic Respiration Concept 2
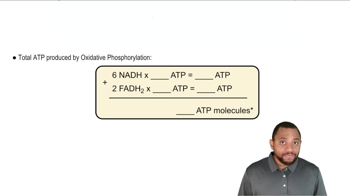
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the final stage of cellular respiration, occurring in the mitochondria, where the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis generate ATP. When oxygen is present, pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, leading to the production of NADH and FADH2 that drive ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation.
Recommended video:
Oxidative Phosphorylation Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution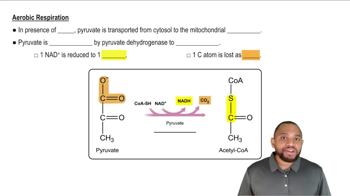

 1:49m
1:49m