Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Decay Series
A decay series refers to a sequence of radioactive decays that a parent isotope undergoes to transform into a stable or different isotope. In this context, the parent isotope decays through a series of alpha (α) and beta (β) decays, resulting in the formation of bismuth-212. Understanding the types of decay and their order is crucial for identifying the parent isotope.
Recommended video:
Alpha and Beta Decay
Alpha decay involves the emission of an alpha particle (two protons and two neutrons), resulting in a decrease in the atomic number by two and the mass number by four. Beta decay, on the other hand, involves the conversion of a neutron into a proton with the emission of a beta particle (an electron), increasing the atomic number by one. Recognizing how these decays affect the isotopes is essential for tracing the decay path back to the parent isotope.
Recommended video:
Isotope Identification
Isotope identification involves determining the specific isotope of an element based on its atomic number and mass number. In the case of bismuth-212, it is important to trace back through the decay series to find the original isotope that leads to its formation. This requires knowledge of the isotopes involved in the decay process and their respective properties.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution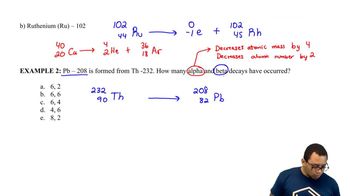



 2:06m
2:06m