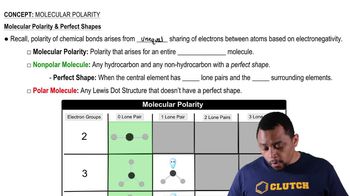
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a chemical bond. The difference in electronegativity between two bonded atoms determines the bond's polarity; a larger difference indicates a more polar bond. For example, oxygen is highly electronegative, which influences the polarity of bonds it forms with other elements.
Recommended video:
Dipole Moment (Simplified) Concept 1
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, typically between nonmetals. The nature of the shared electrons can vary based on the atoms' electronegativities, leading to polar or nonpolar covalent bonds. Understanding the type of covalent bond is essential for determining the bond's polarity and its chemical properties.
Recommended video:
Polarity of Bonds
The polarity of a bond refers to the distribution of electrical charge across the bond, which results from differences in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. A polar bond has a significant charge separation, while a nonpolar bond has an even distribution of charge. Arranging bonds by polarity involves assessing the electronegativity differences and their implications for molecular behavior.
Recommended video:
Molecular Polarity (Simplified) Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:51m
1:51m