Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Metabolic Pathways
Metabolic pathways are sequences of chemical reactions occurring within a cell, where substrates are transformed into products through various enzymatic processes. Understanding these pathways is crucial for identifying how compounds like acetoacetate are converted into 3-hydroxybutyrate, as it involves specific reactions that can be classified into categories such as oxidation and reduction.
Recommended video:
Metabolic Pathways Concept 2
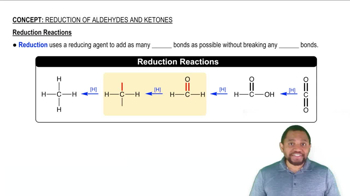
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
Oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions are fundamental chemical processes where the oxidation state of molecules changes. In the context of 3-hydroxybutyrate formation, reduction refers to the gain of electrons or hydrogen, which is essential for converting acetoacetate into 3-hydroxybutyrate, highlighting the importance of these reactions in metabolic transformations.
Recommended video:
Reduction Reactions Concept 1
Functional Group Transformations
Functional group transformations involve changes in the functional groups of organic molecules, which can alter their chemical properties and reactivity. In the case of acetoacetate to 3-hydroxybutyrate, the transformation includes the addition of a hydroxyl group, illustrating how functional group changes are critical in biochemical reactions and classifications.
Recommended video:
Functional Group Priorities Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:29m
1:29m