Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law is a fundamental equation in chemistry that relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas. It is expressed as PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature in Kelvin. This law allows us to predict how a gas will behave under different conditions.
Recommended video:
Charles's Law
Charles's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when pressure is held constant. Mathematically, it can be expressed as V1/T1 = V2/T2. This principle is crucial for understanding how changes in temperature affect the volume of a gas, which is essential for solving the given problem.
Recommended video:
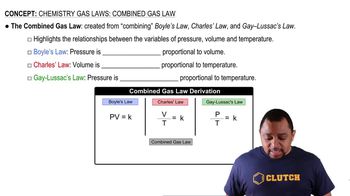
Chemistry Gas Laws: Combined Gas Law
Pressure Conversion
Pressure conversion is the process of changing pressure units from one system to another, such as from atmospheres (atm) to millimeters of mercury (mmHg). In this case, 1 atm is equivalent to 760 mmHg. Understanding how to convert between these units is necessary to apply the Ideal Gas Law and Charles's Law correctly in the context of the problem.
Recommended video:
Conversion Factors (Simplified) Example 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 0:33m
0:33m