Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amides
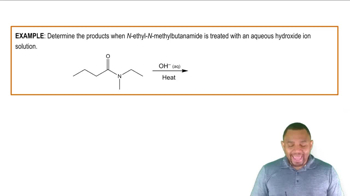
Amides are organic compounds derived from carboxylic acids where the hydroxyl group is replaced by an amine or ammonia. They have the general structure R-CO-NR'R'', where R represents a hydrocarbon chain, and NR'R'' indicates the nitrogen atom bonded to one or more alkyl or aryl groups. Amides are important in various biological processes and are commonly found in proteins.
Recommended video:
Intro to Amides Example 1
Condensed Structural Formula
A condensed structural formula is a way of representing a chemical structure that shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule without depicting all the bonds explicitly. It simplifies the representation by grouping atoms together, often indicating the connectivity of atoms in a linear format. This format is particularly useful for larger molecules, as it provides a clear overview of the structure while saving space.
Recommended video:
Condensed Formula Concept 1
3-Methylbutyramide
3-Methylbutyramide is an amide derived from 3-methylbutanoic acid, where a methyl group is attached to the third carbon of the butyric acid chain. Its condensed structural formula can be represented as CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CO-NH2, indicating the presence of the amide functional group (-CO-NH2) at the end of the carbon chain. Understanding its structure is essential for predicting its chemical behavior and interactions.
Recommended video:
Basic Hydrolysis Example 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 :59m
:59m