Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing energy in the form of ATP. It occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and consists of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The first step involves the phosphorylation of glucose, which is crucial for trapping glucose within the cell and initiating its breakdown for energy production.
Recommended video:
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a molecule, in this case, glucose. This process is catalyzed by the enzyme hexokinase in glycolysis, converting glucose to glucose 6-phosphate. The addition of the phosphate group alters the chemical structure of glucose, making it more polar and preventing it from easily crossing the cell membrane, thus retaining it within the cell.
Recommended video:
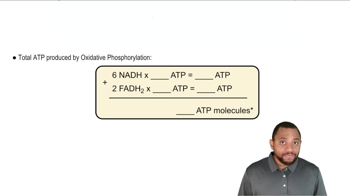
Oxidative Phosphorylation Concept 2
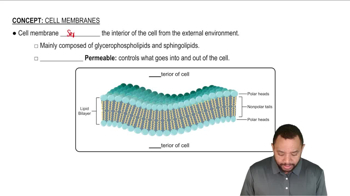
Cell Membrane Permeability
Cell membrane permeability refers to the ability of substances to pass through the cell membrane. The membrane is selectively permeable, allowing certain molecules to enter or exit while restricting others. Since glucose 6-phosphate is charged and larger than glucose, its phosphorylation reduces its ability to diffuse back out of the cell, effectively trapping it inside for further metabolism.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 1:21m
1:21m