Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
ATP Yield in Cellular Respiration
ATP yield refers to the amount of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) produced during metabolic processes, particularly in cellular respiration. Different pathways, such as glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, contribute varying amounts of ATP. Understanding these yields is crucial for analyzing energy production in cells.
Recommended video:
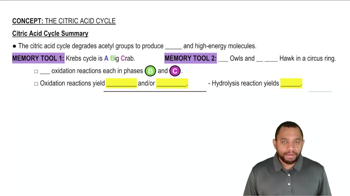
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a key metabolic pathway that occurs in the mitochondria. It processes acetyl CoA to produce electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) and ATP. One complete turn of the cycle generates a specific yield of ATP, which is essential for understanding the overall energy output of cellular respiration.
Recommended video:
Citric Acid Cycle Summary Concept 12
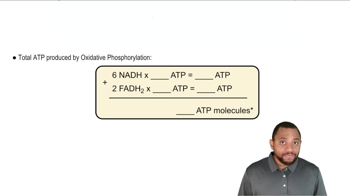
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the final stage of cellular respiration, occurring in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It involves the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis, leading to the production of the majority of ATP in aerobic organisms. The efficiency of this process significantly impacts the total ATP yield from glucose metabolism.
Recommended video:
Oxidative Phosphorylation Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 :50m
:50m