Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cell Membrane Structure
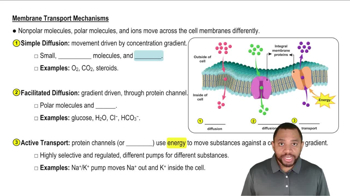
The cell membrane is primarily composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which creates a semi-permeable barrier. This structure allows certain molecules to pass through while restricting others based on size, polarity, and charge. Understanding this structure is crucial for predicting how different metabolites, like carbon monoxide (CO), can traverse the membrane.
Recommended video:
Diffusion
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Small, nonpolar molecules, such as CO, can easily diffuse across the lipid bilayer without the need for transport proteins. This concept is essential for understanding how gases and small metabolites enter or exit cells.
Recommended video:
Oxidative Phosphorylation Example 1
Transport Mechanisms
Transport mechanisms refer to the various ways substances can cross the cell membrane, including passive transport (like diffusion) and active transport. While CO can diffuse passively, other metabolites may require specific transport proteins or energy input to move across the membrane. Recognizing these mechanisms helps in analyzing the behavior of different metabolites in cellular environments.
Recommended video:
Membrane Transport Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 :50m
:50m