Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist. They help visualize the arrangement of electrons and the connectivity of atoms, which is crucial for predicting molecular shapes and properties. Understanding how to draw and interpret Lewis structures is essential for analyzing molecular geometry and polarity.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Ions (Simplified) Concept 1
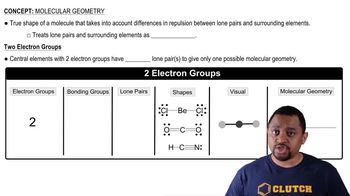
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is determined by the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom, following the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory. Identifying the correct molecular shape is vital for understanding the physical and chemical properties of the substance, including its polarity.
Recommended video:
Molecular Geometry (Simplified) Concept 1
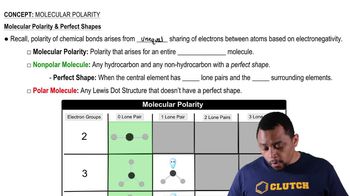
Polarity of Molecules
Polarity in molecules arises from the distribution of electrical charge, which is influenced by the electronegativity of the atoms involved and the molecular geometry. A molecule is polar if it has a net dipole moment due to an uneven distribution of charge, while nonpolar molecules have symmetrical charge distributions. Recognizing whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar is important for predicting its interactions with other substances, such as solubility and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Molecular Polarity (Simplified) Concept 1


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 1:34m
1:34m