Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
mRNA Translation
mRNA translation is the process by which ribosomes synthesize proteins using the information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA sequence is read in sets of three nucleotides, called codons, each of which corresponds to a specific amino acid. This process is essential for converting genetic information into functional proteins.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Translation Concept 1
Amino Acid Codons
Amino acid codons are triplet sequences of nucleotides in mRNA that specify which amino acid will be added during protein synthesis. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or a stop signal, and understanding the genetic code is crucial for translating mRNA into the correct amino acid sequence.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
Amino Acid Abbreviations
Amino acid abbreviations are shorthand notations used to represent amino acids in sequences. They can be either three-letter codes (e.g., Ala for Alanine) or one-letter codes (e.g., A for Alanine). Using these abbreviations allows for a more concise representation of protein sequences, which is particularly useful in scientific communication.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution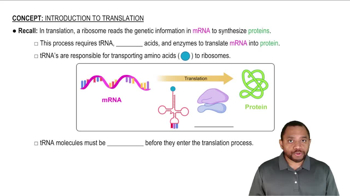



 3:25m
3:25m