Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid contains a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group) that determines its unique properties. Understanding the structure and function of amino acids is essential for grasping how they interact in biochemical reactions, including the formation of cyclic esters.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
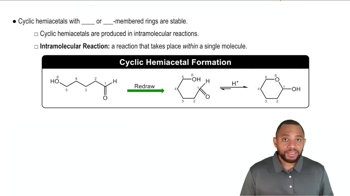
Cyclic Esters (Lactones)
Cyclic esters, also known as lactones, are formed when a hydroxyl group reacts with a carboxyl group within the same molecule, resulting in a ring structure. This intramolecular reaction typically occurs in compounds with both functional groups close together, leading to a stable cyclic form. Lactones are significant in organic chemistry and biochemistry, as they can influence the properties and reactivity of molecules.
Recommended video:
Cyclic Hemiacetals Concept 2
Intramolecular Reactions
Intramolecular reactions occur when a reaction takes place within a single molecule, leading to the formation of new bonds and structures. In the context of amino acids, these reactions can result in the formation of cyclic structures, such as lactones, by bringing functional groups into proximity. Understanding intramolecular reactions is crucial for predicting the behavior of organic compounds and their transformations.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular Forces (Simplified) Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:5m
1:5m