Identify the amino acid carried by tRNAs with the following anticodon sequences.
5′-CUC-3′
For each of the anticodon sequences given in the previous problem, identify the other codon sequence to which it could potentially pair using third base wobble.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Anticodon and Codon Pairing
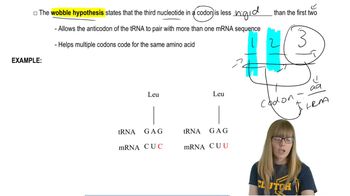
Wobble Hypothesis

Genetic Code Redundancy

Identify the amino acid carried by tRNAs with the following anticodon sequences.
5′-AUG-3′
Identify the amino acid carried by tRNAs with the following anticodon sequences.
5′-GAU-3′
What is the role of codons UAA, UGA, and UAG in translation? What events occur when one of these codons appears at the A site of the ribosome?
Compare and contrast the composition and structure of bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes, identifying at least three features that are the same and three features that are unique to each type of ribosome.
Consider translation of the following mRNA sequence:
5′-...AUGCAGAUCCAUGCCUAUUGA...-3′
Diagram translation at the moment the fourth amino acid is added to the polypeptide chain. Show the ribosome; label its A, P, and E sites; show its direction of movement; and indicate the position and anticodon triplet sequence of tRNAs that are currently interacting with mRNA codons.
