The DNA sequences shown below are from the promoter regions of six bacterial genes. In each case, the last nucleotide in the sequence (highlighted in blue) is the nucleotide that initiates transcription. Determine the consensus sequence for the Pribnow box from these sequences. <>
 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 8 - Molecular Biology of Transcription and RNA Processing
Ch. 8 - Molecular Biology of Transcription and RNA Processing Problem 10
Problem 10What is the role of enhancer sequences in transcription of eukaryotic genes? Speculate about why enhancers are not part of transcription of bacterial genes.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Enhancer Sequences

Transcription in Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes
Gene Regulation

Bacterial and eukaryotic gene transcripts can differ—in the transcripts themselves, in whether the transcripts are modified before translation, and in how the transcripts are modified. For each of these three areas of contrast, describe what the differences are and why the differences exist.
Describe the two types of transcription termination found in bacterial genes. How does transcription termination differ for eukaryotic genes?
Describe the difference between introns and exons.
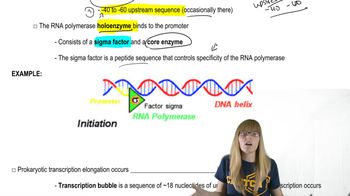
Draw a bacterial promoter and label its consensus sequences. How does this promoter differ from a eukaryotic promoter transcribed by RNA polymerase II? By RNA polymerase I? By RNA polymerase III?
For a eukaryotic gene whose transcription requires the activity of an enhancer sequence, explain how proteins bound at the enhancer interact with RNA pol II and transcription factors bound at the promoter.