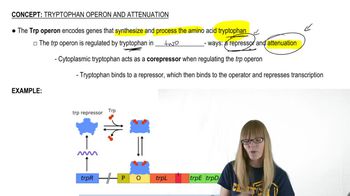
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Repressor
A repressor is a type of regulatory protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, inhibiting the transcription of genes. By blocking RNA polymerase from accessing the promoter region, repressors prevent gene expression. An example is the lac repressor in the lac operon, which binds to the operator region in the absence of lactose, preventing the transcription of genes involved in lactose metabolism.
Recommended video:
Operon
An operon is a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter, allowing for coordinated regulation of gene expression. Operons are common in prokaryotes and enable the bacteria to efficiently respond to environmental changes. The lac operon, for instance, contains genes necessary for lactose utilization and is regulated by the presence or absence of lactose and glucose.
Recommended video:
Transcriptional Regulation
Transcriptional regulation refers to the mechanisms that control the rate of gene transcription, determining how much of a gene's product is produced. This regulation can involve various factors, including transcription factors, repressors, and enhancers, which interact with DNA and RNA polymerase. Effective transcriptional regulation is crucial for cellular responses to environmental signals and developmental processes.
Recommended video: