Textbook Question
Identify the normal functions of the following genes whose mutations are associated with the development of cancer.
RB1 (retinoblastoma)
280
views
 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination
Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination Problem 1
Problem 1 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


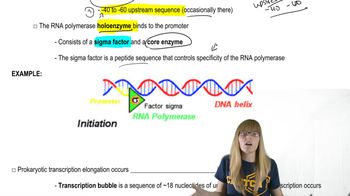
Identify the normal functions of the following genes whose mutations are associated with the development of cancer.
RB1 (retinoblastoma)
Identify the normal functions of the following genes whose mutations are associated with the development of cancer.
Which of these genes would you classify as a proto-oncogene and which as a tumor suppressor gene? Explain your categorization for each gene.
Identify the normal functions of the following genes whose mutations are associated with the development of cancer.
APC (familial adenomatous polyposis)
Identify the normal functions of the following genes whose mutations are associated with the development of cancer.
c-MYC (Burkitt lymphoma)