Textbook Question
Nitrous acid and 5-bromodeoxyuracil (BrdU) alter DNA by different mechanisms. What type of mutation does each compound produce?
293
views
 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination
Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination Problem 3
Problem 3 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

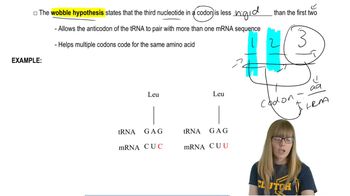

Nitrous acid and 5-bromodeoxyuracil (BrdU) alter DNA by different mechanisms. What type of mutation does each compound produce?
What is the difference between a transition mutation and a transversion mutation?
What are the differences between a synonymous mutation, a missense mutation, and a nonsense mutation?
Explain the following processes involving chromosome mutations and cancer development.
How the chromosome mutation producing the Philadelphia chromosome leads to CML.