Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lac Operon
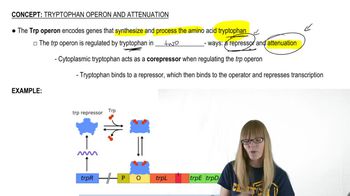
The lac operon is a set of genes in bacteria, specifically E. coli, that are involved in the metabolism of lactose. It consists of structural genes that encode proteins necessary for lactose uptake and breakdown, and it is regulated by a promoter and an operator. Understanding the lac operon is crucial for grasping how bacteria adapt to different energy sources and how gene expression is controlled in response to environmental changes.
Recommended video:
Repressor Molecule
A repressor molecule is a type of protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, inhibiting the transcription of certain genes. In the context of the lac operon, the lac repressor binds to the operator region, preventing RNA polymerase from transcribing the downstream genes when lactose is absent. This mechanism is a key example of negative regulation in gene expression, demonstrating how cells conserve resources by only expressing genes when their products are needed.
Recommended video:
Gene Regulation Mechanisms
Gene regulation mechanisms are processes that control the timing and amount of gene expression in response to internal and external signals. In bacteria, these mechanisms include operons, repressors, and activators, which work together to ensure that genes are expressed only when necessary. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for interpreting experimental results and the conclusions drawn about how specific molecules, like repressors, influence gene expression.
Recommended video: