Textbook Question
How do we know that mutations occur randomly?
723
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

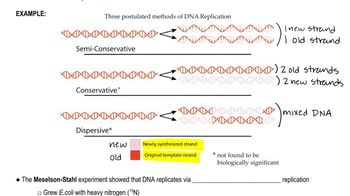

How do we know that mutations occur randomly?
How do we know that certain chemicals and wavelengths of radiation induce mutations in DNA?
How do we know that DNA repair mechanisms detect and correct the majority of spontaneous and induced mutations?
What is a spontaneous mutation, and why are spontaneous mutations rare?
Why would a mutation in a somatic cell of a multicellular organism not necessarily result in a detectable phenotype?
Most mutations are thought to be deleterious. Why, then, is it reasonable to state that mutations are essential to the evolutionary process?