Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
Epistasis and Complementation
Problem 24b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionBlue flower color is produced in a species of morning glories when dominant alleles are present at two gene loci, A and B. (Plants with the genotype have blue flowers.) Purple flowers result when a dominant allele is present at only one of the two gene loci, A or B. (Plants with the genotypes and are purple.) Flowers are red when the plant is homozygous recessive for each gene (i.e., aabb).
If two F₁ plants are crossed, what are the expected phenotypes and frequencies in the F₂?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
In genetics, alleles are different forms of a gene that can exist at a specific locus. Dominant alleles mask the effect of recessive alleles in heterozygous conditions. In the case of the morning glories, the presence of dominant alleles at either or both loci (A or B) results in blue or purple flowers, while the absence of dominant alleles (homozygous recessive) leads to red flowers.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Variations on Dominance
Gene Loci and Epistasis
Gene loci refer to the specific locations of genes on a chromosome. In this scenario, two loci (A and B) interact to determine flower color, demonstrating a form of epistasis where the expression of one gene affects the expression of another. This interaction is crucial for predicting the phenotypes of offspring in genetic crosses, as it influences the overall expression of traits.
Recommended video:
Guided course
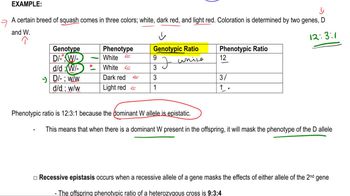
Epistatic Genes
Punnett Square and Phenotypic Ratios
A Punnett square is a tool used in genetics to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a genetic cross. By filling out a Punnett square for the F₁ plants, one can determine the expected phenotypic ratios in the F₂ generation. This method allows for the visualization of how alleles segregate and combine, leading to specific flower colors based on the dominant and recessive alleles present.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square Analysis

 5:05m
5:05mWatch next
Master Complementation with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning